What Type Of Macromolecule Contains Fats Lipids And Steroids
Macromolecules are the building blocks of life that are essential for the proper functioning of our body. They can be…
Macromolecules are the building blocks of life that are essential for the proper functioning of our body. They can be classified into four categories, namely carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids. While carbohydrates and proteins are widely known, lipids are often overlooked despite their vital role in our body.
Lipids are a diverse group of macromolecules that include fats, oils, waxes, and steroids. They are essential for energy storage, insulation, and protection of vital organs in our body. However, not all lipids are created equal, and in this article, we will focus on the types of lipids that contain fats, lipids, and steroids, and their importance in our body.
What Type of Macromolecule Contains Fats, Lipids, and Steroids?
Introduction
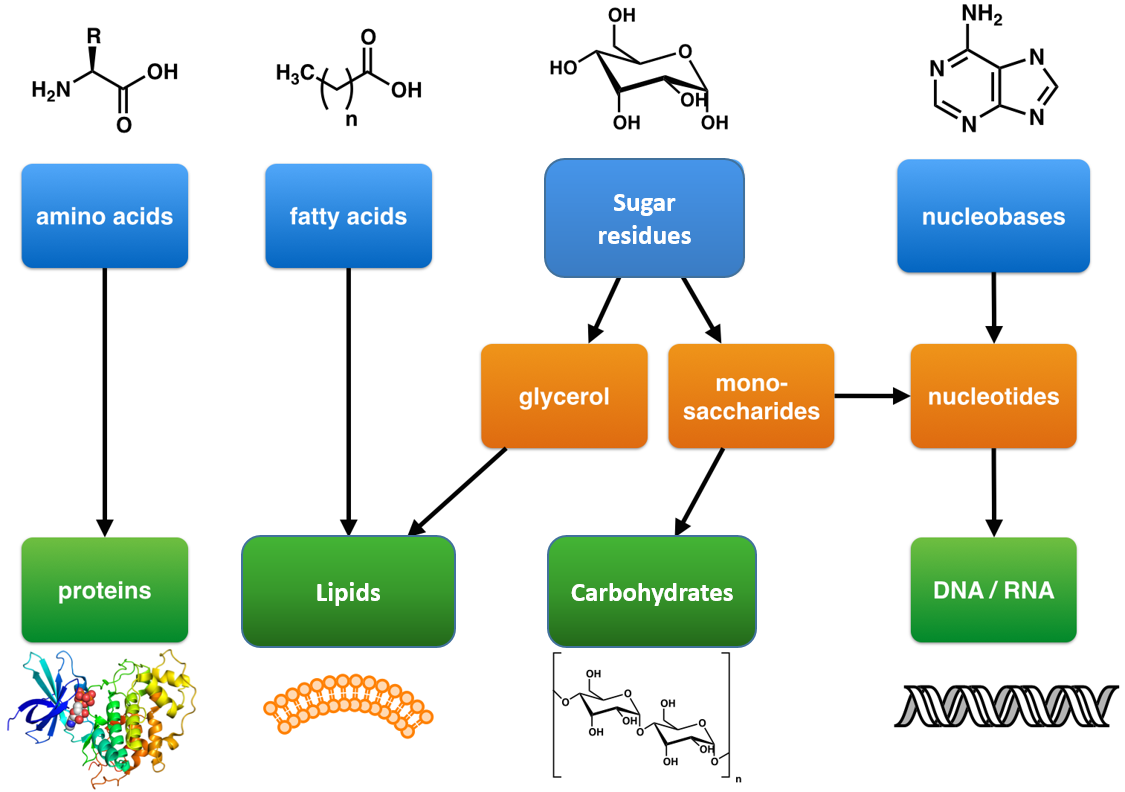
Macromolecules are large molecules that are essential for life. They are made up of smaller units called monomers, which are joined together to form polymers. There are four main types of macromolecules found in living organisms: carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids. Lipids are unique among the macromolecules because they are not polymers. Instead, they are made up of individual molecules that are similar in structure but different in function.
What are Lipids?
Lipids are a diverse group of molecules that are insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents. They include fats, oils, waxes, steroids, and phospholipids. Fats and oils are used for energy storage, while waxes are used for protection. Steroids play a variety of roles in the body, including acting as hormones and serving as the building blocks of cell membranes. Phospholipids are a major component of cell membranes and are essential for their structure and function.
Lipids are made up of three types of molecules: glycerol, fatty acids, and a variety of other molecules, including cholesterol. Glycerol is a three-carbon molecule with a hydroxyl group attached to each carbon. Fatty acids are long hydrocarbon chains with a carboxyl group attached to one end. The carboxyl group makes fatty acids acidic, hence their name. Other molecules, such as cholesterol, are added to lipids to give them their unique properties and functions.
Types of Lipids
There are several types of lipids, each with its own unique structure and function. These include:
- Fats: Fats are used for energy storage in the body. They are made up of one glycerol molecule and three fatty acid molecules. Fats can be saturated or unsaturated, depending on the number of double bonds in the fatty acid chains.
- Oils: Oils are similar to fats but are liquid at room temperature. They are also used for energy storage.
- Waxes: Waxes are used for protection in plants and animals. They are made up of one long-chain fatty acid and one long-chain alcohol.
- Steroids: Steroids are a class of lipids that have a unique four-ring structure. They include hormones such as testosterone and estrogen, as well as cholesterol, which is a major component of cell membranes.
- Phospholipids: Phospholipids are a major component of cell membranes. They are made up of one glycerol molecule, two fatty acid molecules, and one phosphate group. The phosphate group makes one end of the molecule hydrophilic (water-loving) and the other end hydrophobic (water-hating).
Benefits of Lipids
Lipids are essential for life and play a variety of important roles in the body. Some of the benefits of lipids include:
- Energy storage: Fats and oils are used for energy storage in the body. They are a concentrated source of energy and can be broken down quickly to release energy when needed.
- Protection: Waxes are used for protection in plants and animals. They help to prevent water loss and protect against predators and parasites.
- Structural support: Phospholipids are a major component of cell membranes and are essential for their structure and function. They help to maintain the integrity of the cell membrane and regulate the movement of molecules in and out of the cell.
- Hormones: Steroids, such as testosterone and estrogen, are hormones that play a variety of roles in the body, including regulating metabolism, growth, and development.
- Insulation: Fats and oils can also be used as insulation. They help to maintain body temperature by reducing heat loss.
Lipids vs. Other Macromolecules
Lipids are unique among the macromolecules in that they are not polymers. Carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids are all made up of repeating units called monomers, which are linked together to form polymers. Lipids, on the other hand, are made up of individual molecules that are similar in structure but different in function.
Another difference between lipids and other macromolecules is their solubility. Carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids are all soluble in water, while lipids are not. This makes lipids useful for functions such as energy storage and insulation, which require molecules that are not easily transported by water.
Conclusion
Lipids are a diverse group of molecules that play a variety of important roles in the body. They are unique among the macromolecules in that they are not polymers and are insoluble in water. Lipids include fats, oils, waxes, steroids, and phospholipids, each with its own unique structure and function. Lipids are essential for life and are used for energy storage, protection, structural support, hormone production, and insulation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions related to macromolecules and their components.
What are macromolecules?
Macromolecules are large molecules composed of smaller subunits. The four main types of macromolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. These molecules are essential to life and play a variety of important roles in biological processes.
Carbohydrates are composed of simple sugars, lipids are composed of fatty acids and glycerol, proteins are composed of amino acids, and nucleic acids are composed of nucleotides.
What is the function of lipids in the body?
Lipids have several important functions in the body. They are a major source of energy storage and insulation, helping to regulate body temperature. Lipids also play a role in cell membrane structure and function, acting as a barrier to protect the cell from its environment. Additionally, lipids are involved in the production of hormones and other signaling molecules.
Examples of lipids include fats, oils, waxes, and steroids.
What are steroids and how are they related to lipids?
Steroids are a type of lipid that have a specific structure composed of four rings of carbon atoms. They are important signaling molecules in the body, regulating a variety of physiological processes. Steroids are derived from cholesterol, which is also a type of lipid.
Lipids, including fats and steroids, are nonpolar molecules that are insoluble in water. They are composed of long hydrocarbon chains that make them hydrophobic, or water-fearing. This property allows them to serve as a barrier in cell membranes and to store energy efficiently.
What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fats?
Saturated fats are solid at room temperature and are typically found in animal products such as meat and dairy. They are considered to be less healthy than unsaturated fats because they can raise cholesterol levels in the blood. Saturated fats have no double bonds between their carbon atoms.
Unsaturated fats are liquid at room temperature and are typically found in plant-based foods such as nuts, seeds, and oils. They are considered to be healthier than saturated fats because they can lower cholesterol levels in the blood. Unsaturated fats have at least one double bond between their carbon atoms.
What role do lipids play in the digestive system?
Lipids are an important source of energy for the body, but they are not soluble in water and cannot be transported through the bloodstream on their own. In order to be absorbed by the body, lipids must first be broken down into smaller molecules by enzymes in the digestive system.
Once broken down, lipids are transported through the lymphatic system and eventually enter the bloodstream. From there, they can be used as a source of energy or stored in adipose tissue for later use.
In conclusion, fats, lipids, and steroids are all examples of macromolecules that are grouped together because of their chemical and physical properties. These molecules are essential to the proper functioning of many systems in the body, including the nervous system, immune system, and cardiovascular system.
Fats, for example, are important for energy storage and help to insulate and protect the body’s vital organs. Lipids, on the other hand, play a crucial role in cell membranes and are involved in many metabolic processes. Steroids, such as cholesterol, are a type of lipid that can have both positive and negative effects on the body depending on their concentration.
In summary, the macromolecule that contains fats, lipids, and steroids is the lipid macromolecule. This diverse group of molecules plays a critical role in maintaining the health and function of the body, and understanding their structure and function is essential for developing effective treatments for a variety of diseases and disorders.






