What Type Of Covalent Bond Is Found In Steroids
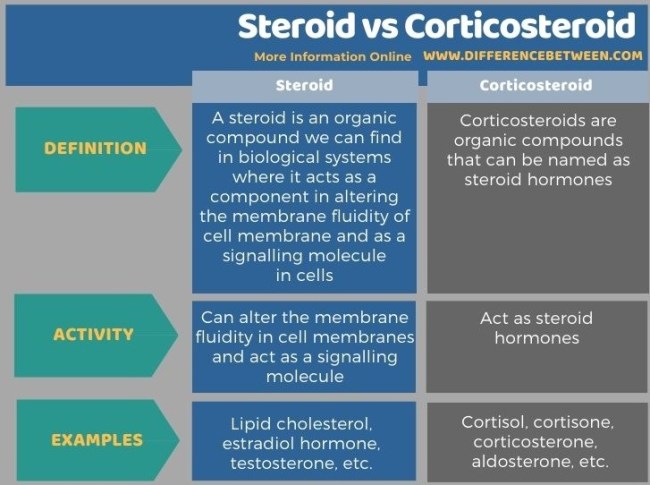
Steroids are a group of organic molecules that play a crucial role in the body’s biochemical processes. They are widely…
Steroids are a group of organic molecules that play a crucial role in the body’s biochemical processes. They are widely known for their use in the sports industry to enhance athletic performance. However, steroids have several other functions, such as regulating metabolism and immune response. Covalent bonds are responsible for holding these complex molecules together, but what type of covalent bond is found in steroids?
The covalent bond found in steroids is known as a carbon-carbon bond. This bond is formed when two carbon atoms share electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration. The carbon-carbon bond is essential in the structure of steroids as it allows for the formation of complex molecular structures that are crucial for their biological function. In this article, we will explore the different types of steroids and how the carbon-carbon bond contributes to their unique properties.
Understanding the Covalent Bond in Steroids
Steroids are organic compounds that are widely used in the medical and sports fields. They are made up of four fused rings, each containing various functional groups. The covalent bond in steroids is crucial to their stability and function. In this article, we will discuss the type of covalent bond found in steroids.
The Basics of Covalent Bonding
Covalent bonding is a type of chemical bonding that involves the sharing of electrons between two atoms. The electrons are shared in such a way that they form a stable molecule. Covalent bonds are stronger than ionic bonds and are generally found in non-metallic substances.
Types of Covalent Bonds
There are two types of covalent bonds, polar and nonpolar. A polar covalent bond occurs when two atoms with different electronegativities share electrons. The electrons are pulled closer to the more electronegative atom, creating a partial positive and partial negative charge. In contrast, a nonpolar covalent bond occurs when two atoms with similar electronegativities share electrons equally.
The Covalent Bond in Steroids
Steroids are composed of four fused rings, each containing various functional groups. The covalent bond found in steroids is a nonpolar covalent bond. The bond is formed between carbon and hydrogen atoms and is known as a sp3 hybridization. This bond is strong and stable, providing the necessary structure for the steroid molecule.
Benefits of Covalent Bonding in Steroids
The covalent bond in steroids provides several benefits. One of the main benefits is stability. The nonpolar covalent bond is strong and does not break easily, allowing the steroid molecule to maintain its shape and function. Additionally, the covalent bond provides the necessary structure for the steroid molecule to interact with other molecules in the body.
Comparison to Other Types of Covalent Bonds
Compared to polar covalent bonds, nonpolar covalent bonds are less reactive. This is beneficial for steroids as they need to remain stable and not react with other molecules in the body. Additionally, nonpolar covalent bonds are less likely to form hydrogen bonds, which can interfere with the function of the steroid molecule.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the covalent bond found in steroids is a nonpolar covalent bond. This bond provides stability and structure to the steroid molecule, allowing it to function properly in the body. Understanding the type of covalent bond found in steroids is important for understanding their function and potential benefits.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a covalent bond?
A covalent bond is a type of chemical bond formed by the sharing of electrons between two atoms.
Covalent bonds can be polar or nonpolar. Polar covalent bonds are formed when electrons are shared unequally between atoms with different electronegativities. Nonpolar covalent bonds are formed when electrons are shared equally between atoms.
What is a steroid?
Steroids are a type of organic molecule that have a characteristic structure of four fused rings.
Steroids are important in the body because they act as hormones, which regulate many physiological processes.
What are the different types of covalent bonds?
There are two main types of covalent bonds: polar covalent bonds and nonpolar covalent bonds.
Polar covalent bonds are formed when electrons are shared unequally between atoms with different electronegativities. Nonpolar covalent bonds are formed when electrons are shared equally between atoms.
What type of covalent bond is found in organic molecules?
Organic molecules typically contain nonpolar covalent bonds. This is because organic molecules are composed of carbon and hydrogen atoms, which have similar electronegativities and therefore share electrons equally.
Nonpolar covalent bonds are also found in other molecules that contain similar atoms, such as nitrogen and oxygen.
What type of covalent bond is found in steroids?
Steroids contain both polar and nonpolar covalent bonds. The four rings that make up the structure of steroids are held together by nonpolar covalent bonds, while the functional groups attached to the rings are held together by polar covalent bonds.
The specific type of covalent bond found in steroids depends on the functional group attached to the rings. For example, the hydroxyl group (-OH) is a polar functional group that forms polar covalent bonds with the rings.
Covalent bonds | Molecular and ionic compound structure and properties | AP Chemistry | Khan Academy
In conclusion, steroids are a group of compounds that contain four fused rings of carbon atoms. These rings are held together by covalent bonds, which are formed when two atoms share a pair of electrons. The type of covalent bond found in steroids is known as a “single covalent bond,” which means that each carbon atom is sharing one electron with another carbon atom.
The single covalent bond found in steroids is unique because it allows the molecule to maintain its shape and structure. This is important because the shape of a molecule determines its function. For example, the shape of the steroid molecule allows it to bind to specific receptors in the body, which can have a variety of effects on different tissues and organs.
Overall, the type of covalent bond found in steroids plays a crucial role in their function and biological activity. Understanding the structure of these compounds and the bonds that hold them together is important for developing new drugs and treatments for a variety of medical conditions. With further research and exploration, we can continue to unlock the secrets of these fascinating molecules and their impact on the human body.